
The natives habitats destruction impacts on these people health, Making them susceptible to diseases brought by non-indigenous.

The natives habitats destruction impacts on these people health, Making them susceptible to diseases brought by non-indigenous.
The native habitats destruction has a significant impact on the indigenous people's health. These communities are susceptible to diseases brought by non-indigenous people and they often live in remote areas and difficult to access. As a result, are susceptible to diseases as malaria, tuberculosis, respiratory infections, hepatitis and sexually transmitted diseases.




Since the foundation of the National Indian Foundation, in 1967, many organizations and governamental organs have been being responsibles for indigenous people care.
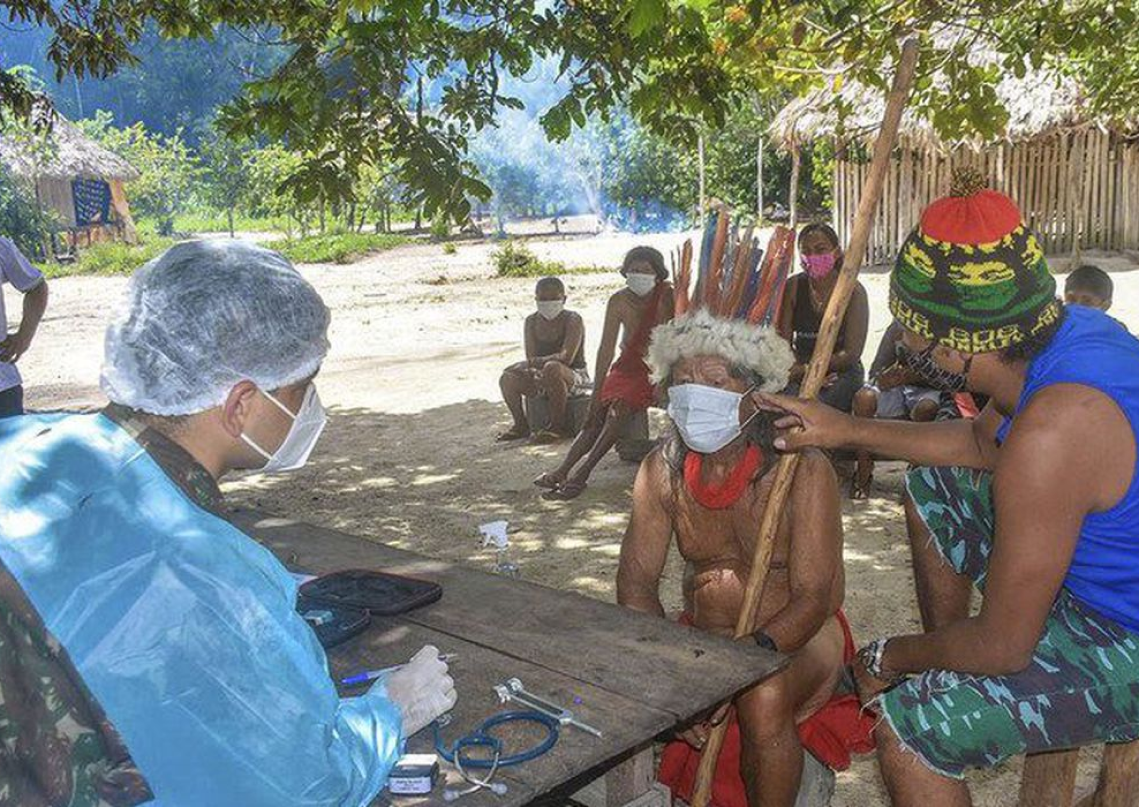
However, the sanitary situation in the villages is rarely positive. In 1999, were implemented by a descentralization care politic, reducing the States' direct action and establishing 34 Special Indigenous Health Districts (SIHD), which produced positve results.

The Special Indigenous Health Districts is responsible for caring of simple cases, while the more complex incidents are care in the regional hospitals.

The social control is exercised through the Indigenous Health Council, which ensures their participation in the management of Special Indigenous Health Districts.
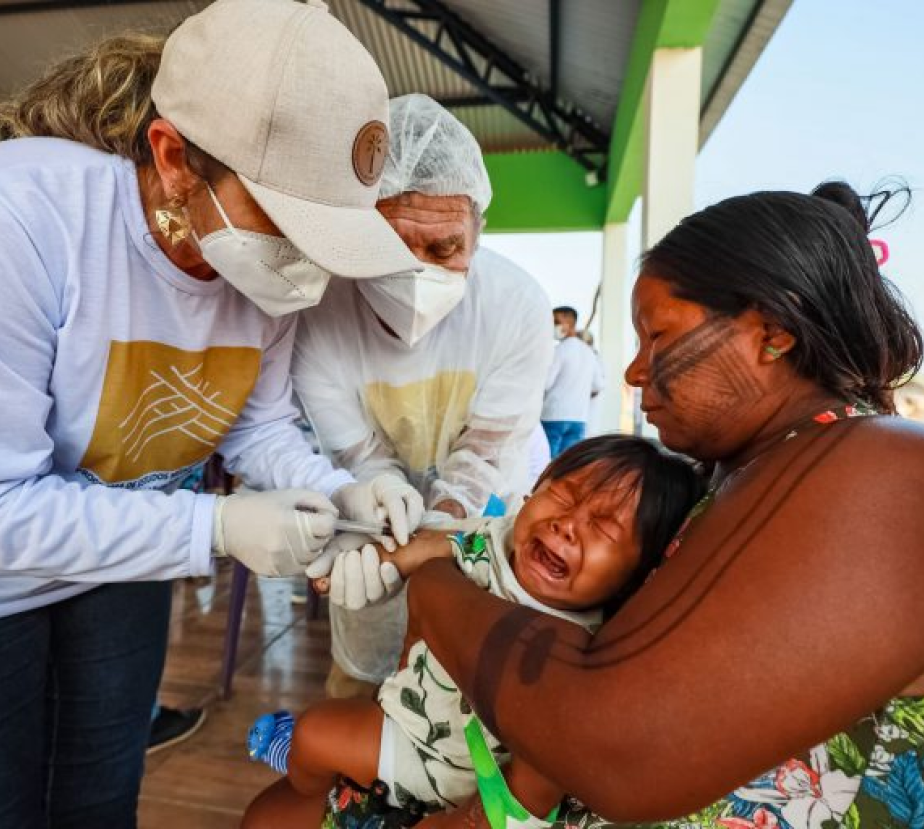
The relation between indigenous people and the Special Indigenous Health Districts's managers is tense and has many problems related to the resources use and management.
It's important to emphasize that the biodiversity lost also has a big impact in the human health and in the spread of disease. The habitat changes makes the infected species more common and make them dominate the health species.