Cultivation
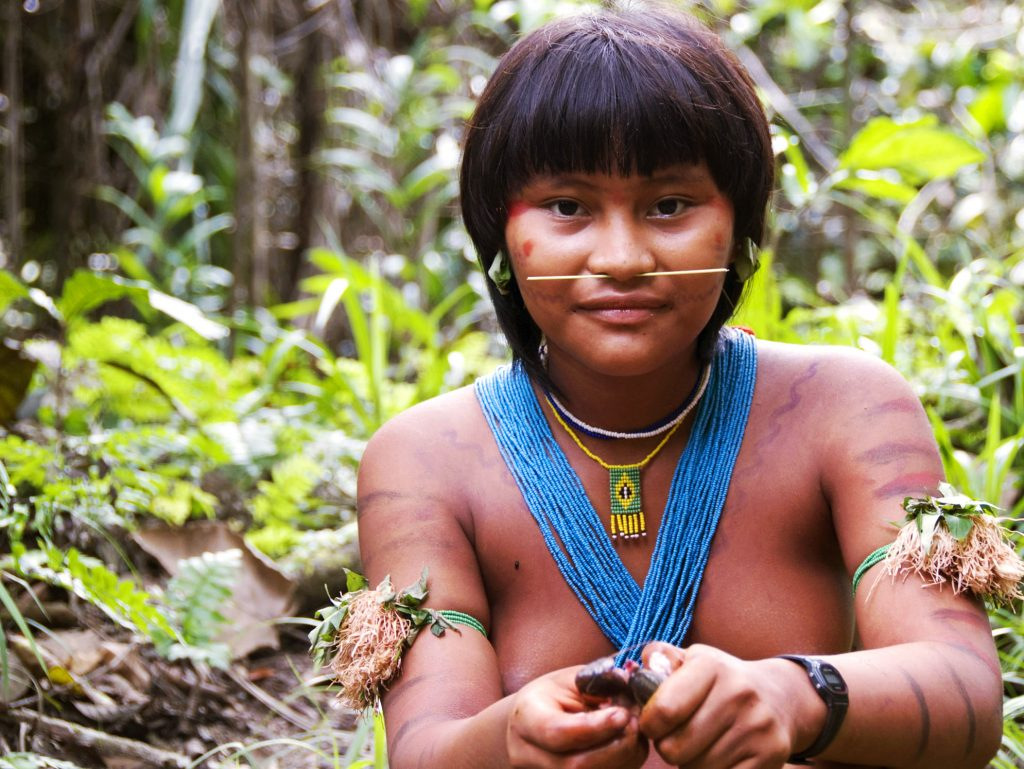
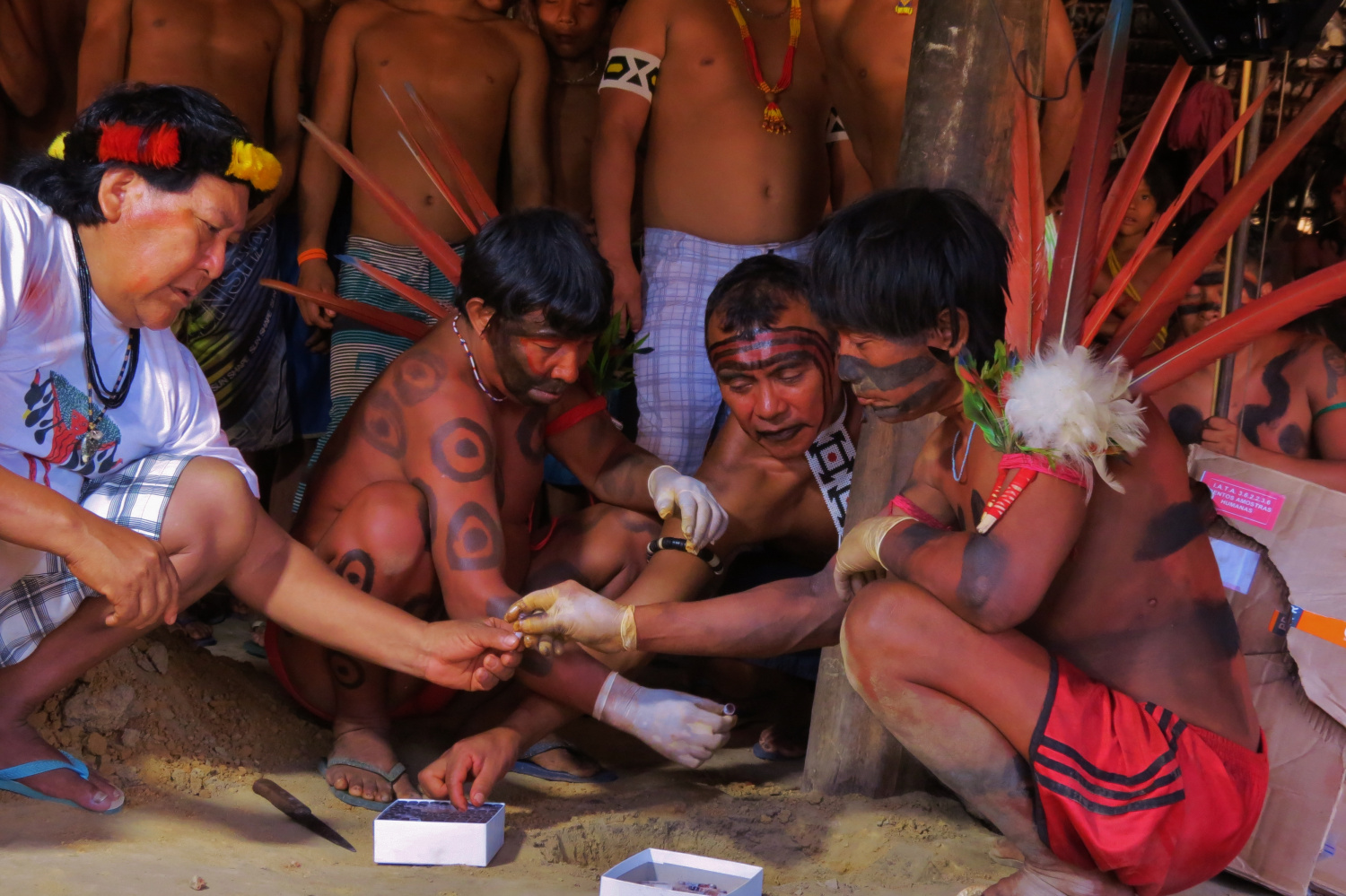
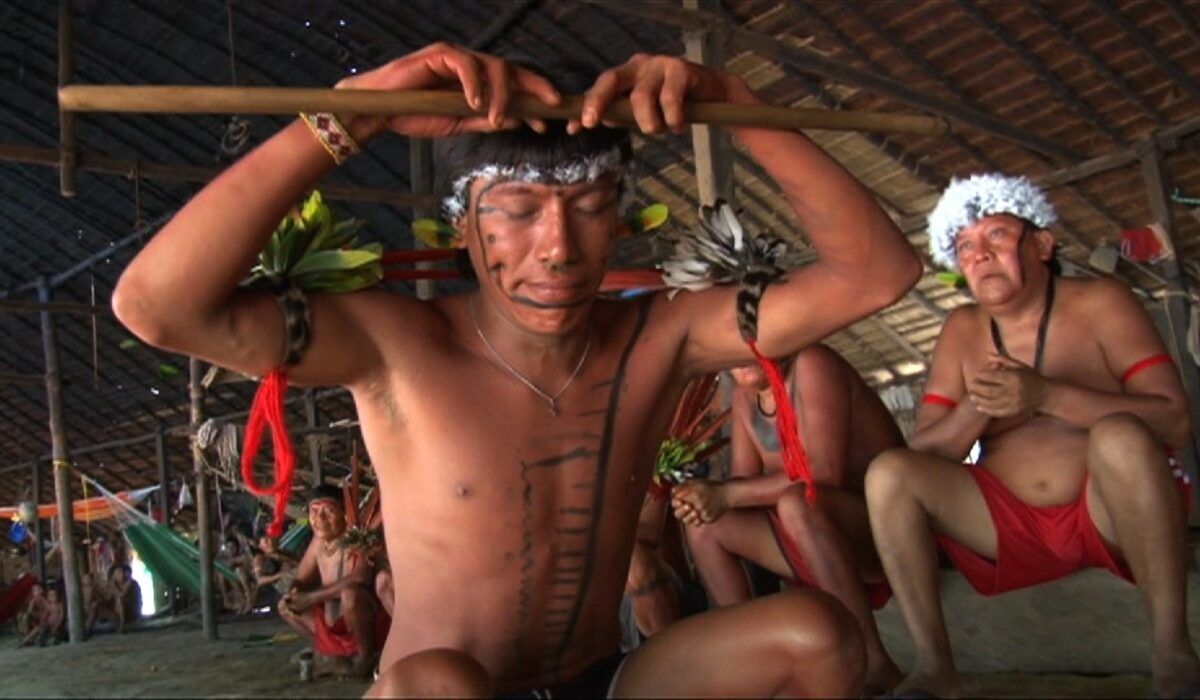
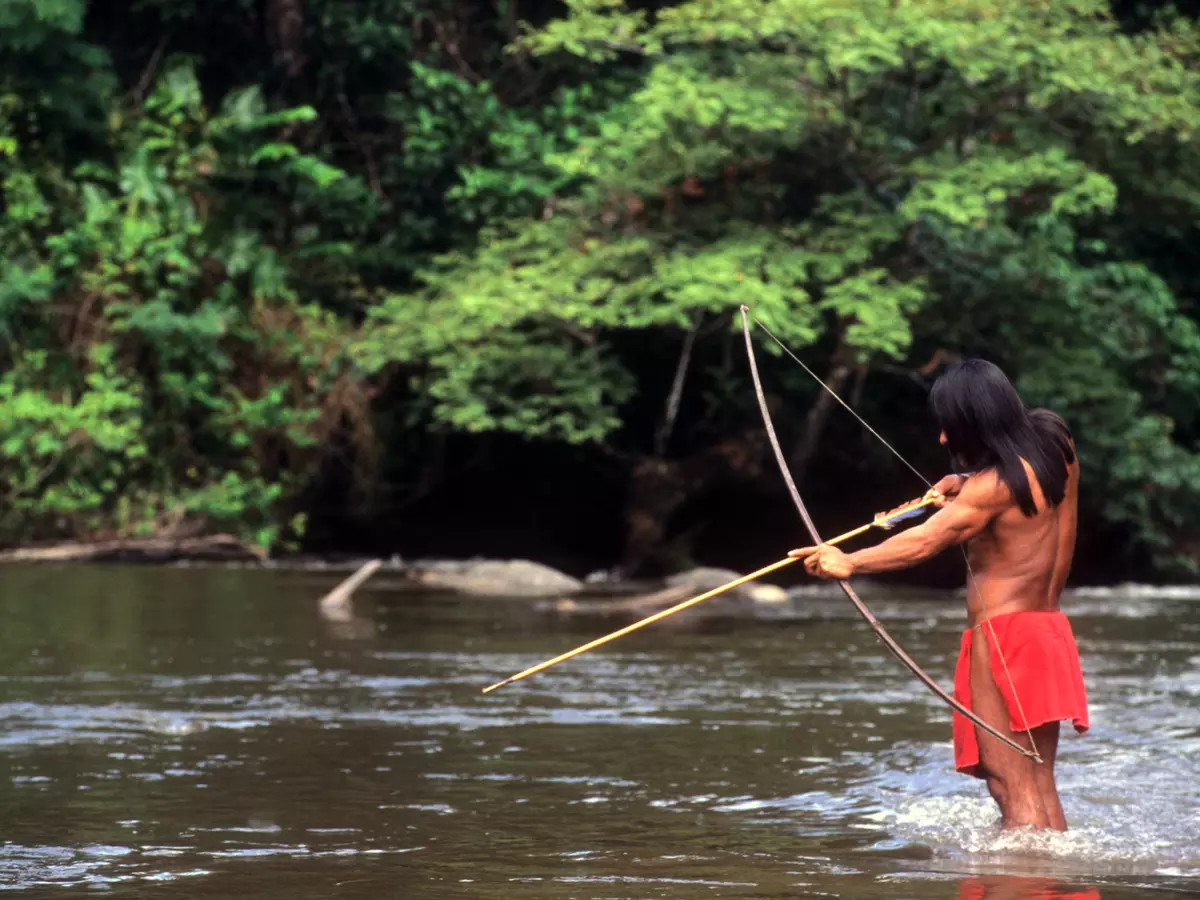
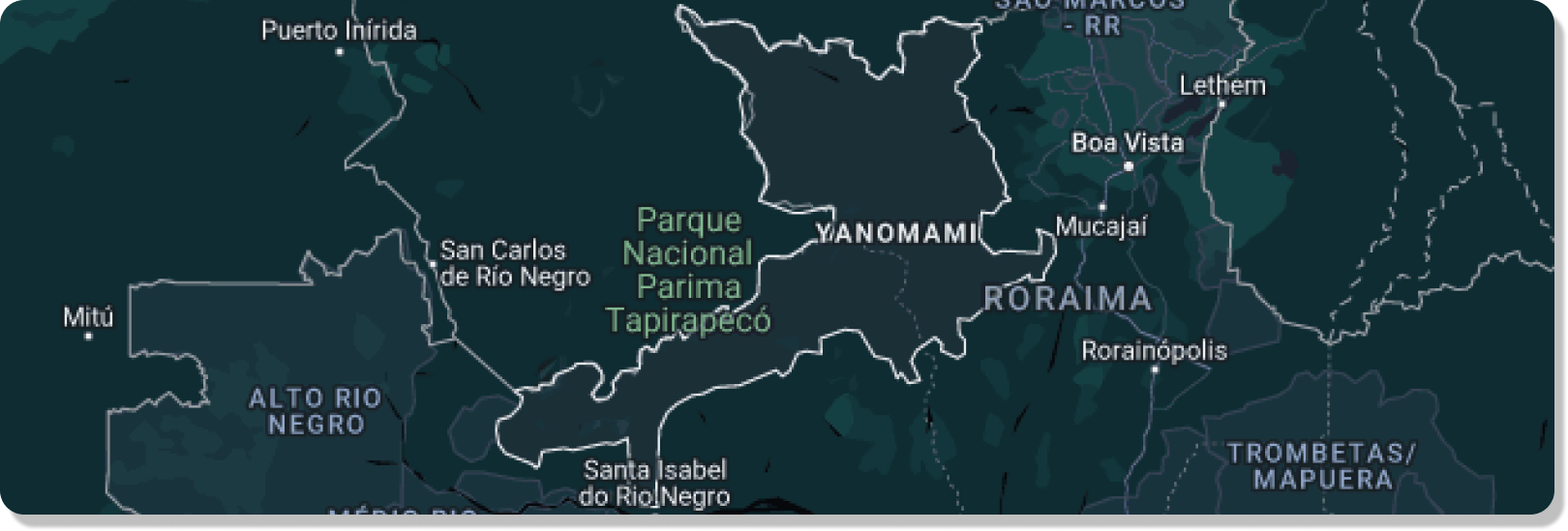
The Yanomami are a group of South American indigenous peoples who live in the northern region of the Amazon rainforest.They eat a variety of foods, such as wild honey, bananas, corn, manioc, fruit, seeds, birds, deer, armadillos, nuts and monkeys.While the men hunt, the women are involved in the harvest or help with the planting.
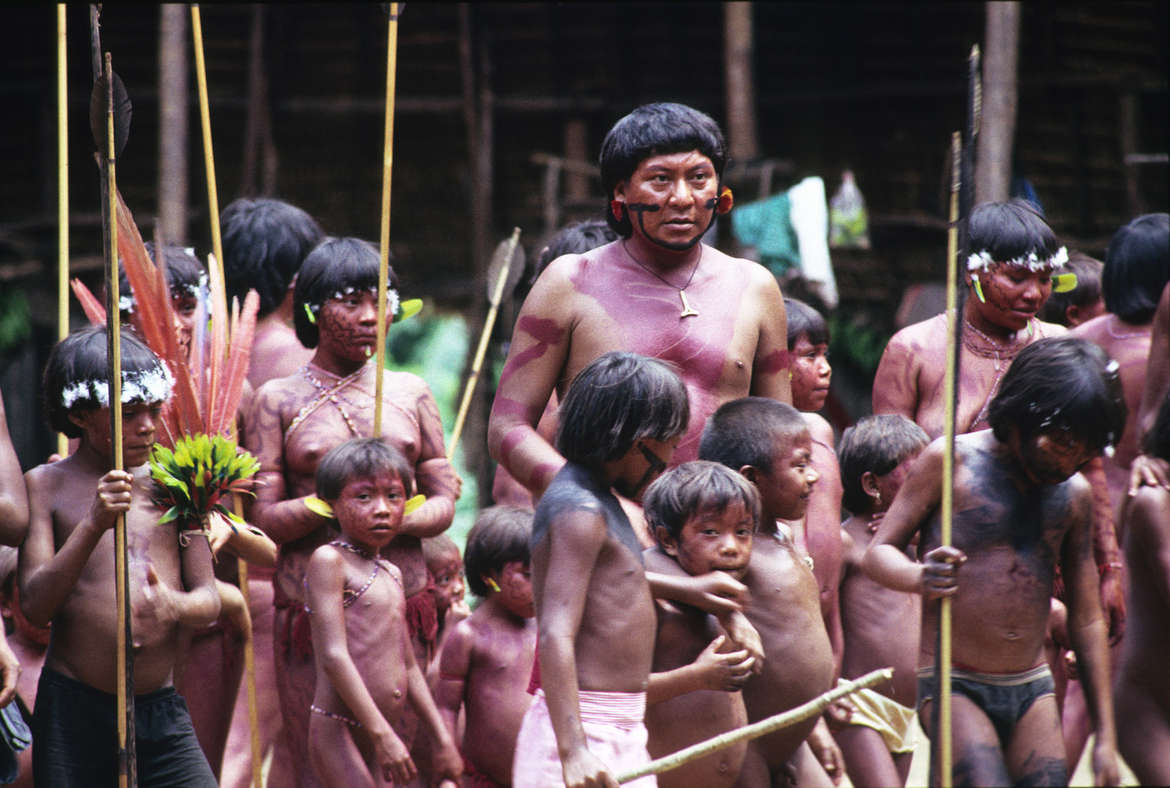
In the Amazon rainforest, people hunt animals. However, when an animal is killed, the meat is not consumed by the people. Instead, they share it with friends and neighbors. This hunter receives the meat from other hunters.
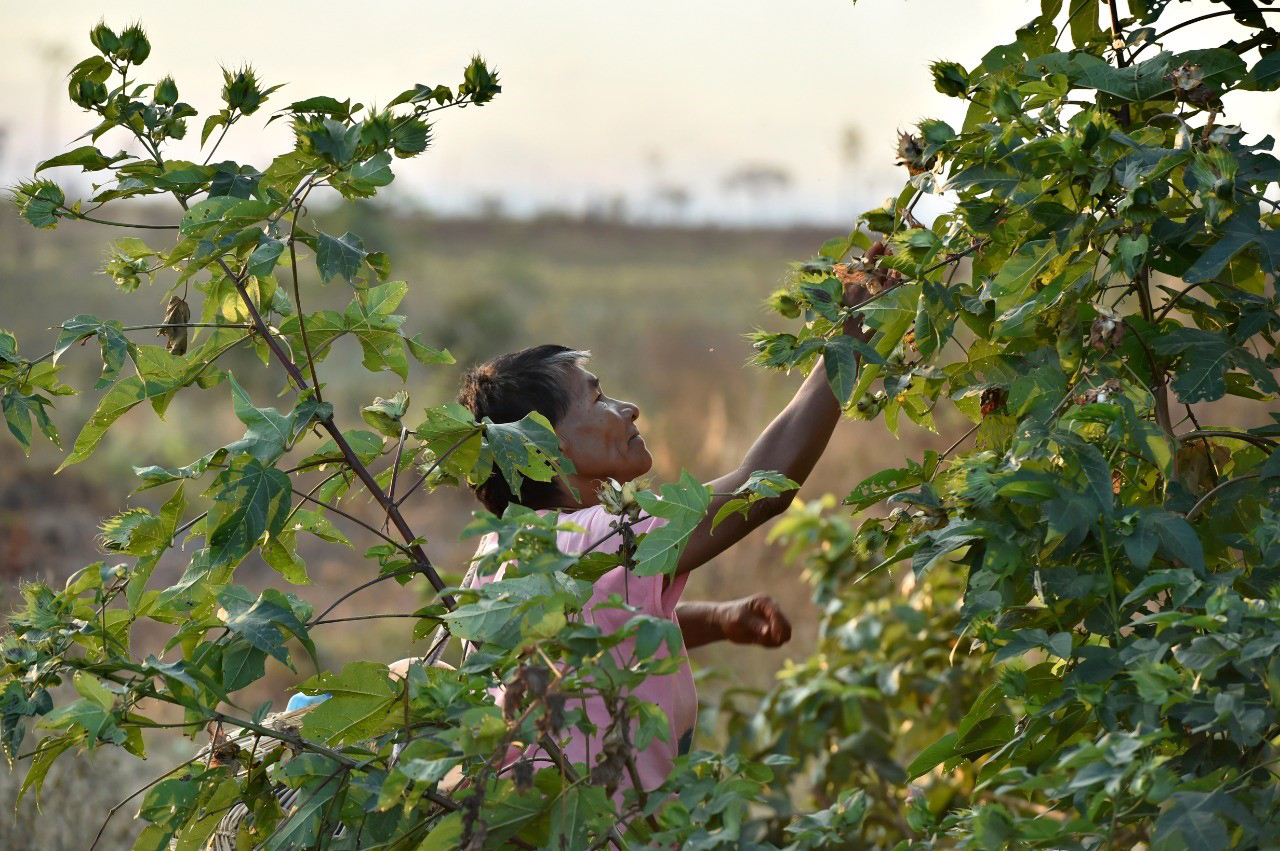
In the gardens, women take responsibility for growing crops such as corn or manioc. Meanwhile, farmers cultivate around 60 different types of plants, including cotton and tobacco. Approximately 80% of the food eaten by humans is produced in flower beds.