History
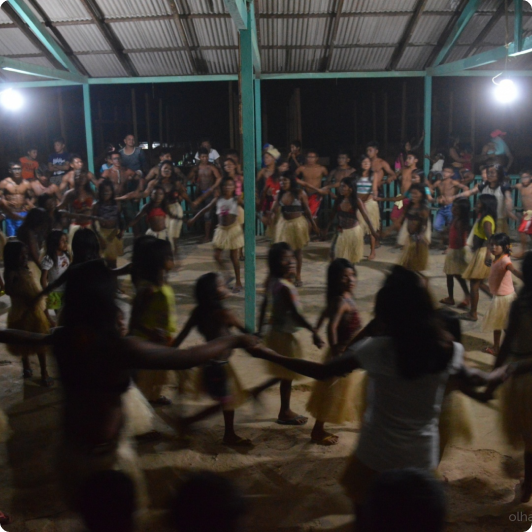
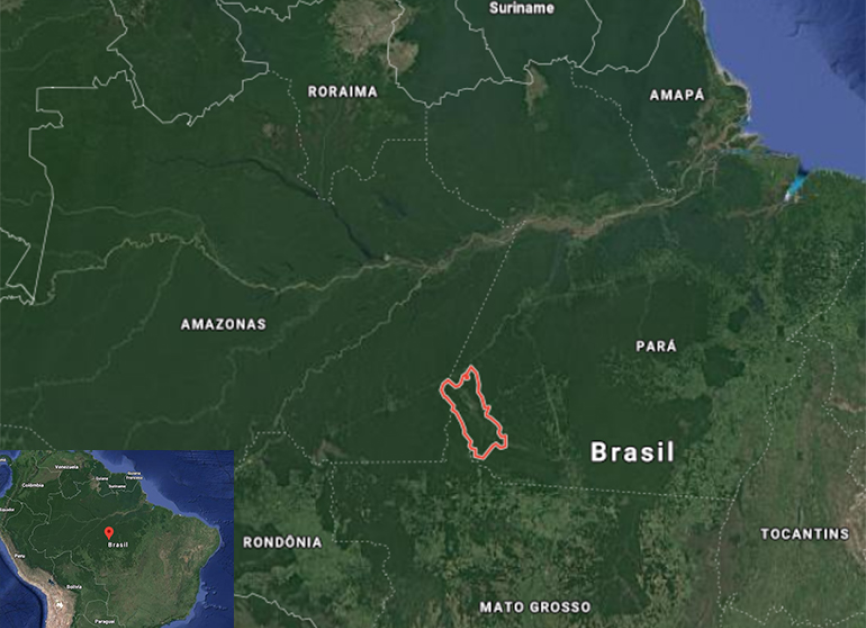
The Munduruku are warrior people which dominate culturally the Tapajós Valley, which in the first times in contact on the 19th century was known as Mundurukânia.
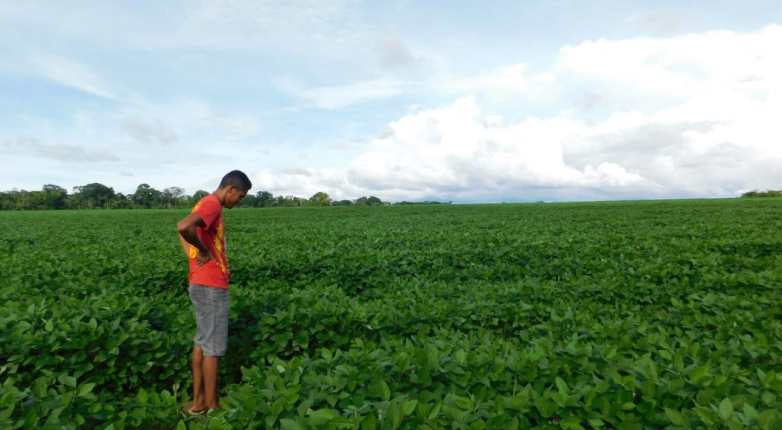
Nowadays, their contemporary battles aim to ensure their territorial integrity, threatened by the pressure of the illegal gold mining, of the hydroelectric projects and of the contruction of the main Tapajós waterway.
The sociolinguistics situation is diverse, because of some different moments on the history of the contact with the colonial fronts and in the reality of dispersion for different geographical spaces of these people.
The people who lives on the little villages on the margins of the Tapajós' river is mainly bilingual.